Wang Laboratory
 Epigenetic Regulation and Neurodegeneration
Epigenetic Regulation and Neurodegeneration
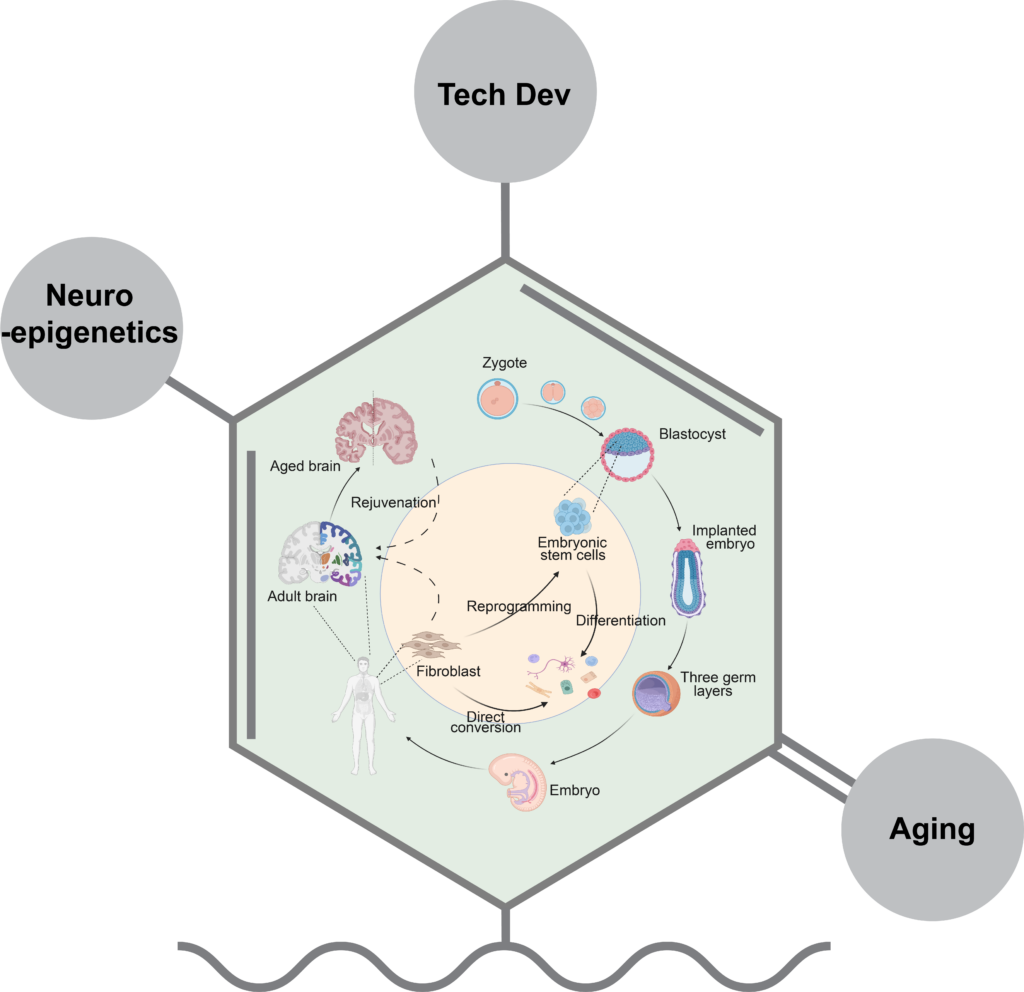
The brain is one of the most intricate and vital tissues for studying a host of biological functions, including cellular diversity. Epigenetic mechanisms are central players in orchestrating cellular differentiation and brain development. These processes encompass DNA methylation, histone modifications and chromatin remodeling, among others.
The Wang Lab aims to answer three fundamental questions with the goal of advancing understanding of epigenetic regulation of brain development and its therapeutic potential for neurodegenerative disorders:
- What determines epigenetic regulation in brain cell heterogeneity?
- How do DNA/RNA/chromatin modalities interact in Alzheimer’s disease and other age-related neurodegenerative conditions?
- Can we develop functional tools that target cell types and manipulate epigenetic regulation?
Understanding the molecular principles of epigenetic crosstalk will provide fresh insights to neurodevelopment and neurodegenerative disorders. However, traditional methods struggle to present multiple layers of biological events from a single cell in a scalable manner.
To address these challenges, the Wang Lab will develop innovative single cell multi-omics technologies and utilize these methods to capture layers of epigenetic regulation and identify age- and neurodegeneration-related gene and cis- regulatory elements (CREs) in human cellular models. We also aim to design tools that target specific brain cell types and perturb epigenetic regulation related to aging and neuronal degeneration in mice models.
News & Publications
Learn MoreChien JF, Liu H, Wang BA, Luo C, Bartlett A, Castanon R, Johnson ND, Nery JR, Osteen J, Li J, Altshul J, Kenworthy M, Valadon C, Liem M, Claffey N, O’Connor C, Seeker LA, Ecker JR, Behrens MM, Mukamel EA. 2024. Cell-type-specific effects of age and sex on human cortical neurons. Neuron 15(7):2524 –2539.e5.
Wang BA*, Jones JR*, Zhou J, Tian* W, Wu Y, Wang W, Berube P, Bartlett A, Castanon R, Nery JR, Chen H, Kenworthy M, Altshul J, Valadon J, Wang Y, Kang A, Goodman R, Liem M, Claffey N, O’Connor C, Metcalf J, Luo C, Gage FH, Ecker JR. Pre-print. Epigenome erosion in Alzheimer’s disease brain cells and induced neurons. bioRxiv.
Liu H, Zeng Q, Zhou J, Bartlett A, Wang BA, Berube P, Tian W, Kenworthy M, Altshul J, Nery JR, Chen H, Castonon RG, Zu S, Li YE, Lucero J, Osteen JK, Pinto-Duarte A, Lee J, Rink J, Cho S, Emerson N, Nunn M, O’Connor C, Wu Z, Stoica I, Yao Z, Smith KA, Tasic B, Luo C, Dixon JR, Zeng H, Ren B, Behrens MM, Ecker JR. 2023. Single-cell DNA methylome and 3D multi-omic atlas of the adult mouse brain. Nature 624:366–377.
Our Impact
We’re raising thousands to save millions.
We’re turning hope into action for the millions of people around the world affected by diseases like cancer and Parkinson’s. Find out how you can help us make a difference.
- 122 peer-reviewed papers published in 2024, 63 of which were in high-impact journals
- 15 VAI-SU2C Epigenetics Dream Team clinical trials launched to date
- 10 clinical trials co-funded by VAI & Cure Parkinson's (out of 41 total International Linked Clinical Trials Program trials)
Bang-An Wang, Ph.D.
Assistant Professor, Department of Neurodegenerative Science
Areas of Expertise
Genetics, Epigenetics, Brain Development, Neurodegeneration, Multi-omics, Technology Development
Biography
Dr. Bang-An Wang is a geneticist whose research weaves together experimental and computational approaches to explore epigenetics in brain development and neurodegeneration.
He earned his B.S. in biochemistry from Shandong University and his Ph.D. in biochemistry and molecular biology from the Chinese Academy of Sciences. As a graduate student in the lab of Dr. Guo-liang Xu, Dr. Wang identified dysfunction in the Lefty-Nodal pathway as the molecular mechanism underlying embryonic developmental defects caused by the disrupted DNA demethylation pathway.
In 2016, Dr. Wang joined the lab of Dr. Joseph Ecker at Salk Institute for Biological Studies, where he held roles as a postdoctoral fellow and a staff scientist. While at Salk, he investigated epigenetic regulation of brain cell heterogeneity and its effects on neurodevelopment and neurodegeneration. Dr. Wang co-developed snmCAT-seq, a novel, robust single cell multi-omics method that enables capture of methylome, transcriptome and open chromatin within one cell. snmCAT-seq has enabled discovery across numerous high-impact projects that explore cell diversity in the brain, including the National Institutes of Health BRAIN Initiative, the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative Human Cell Atlas and the American Heart Association-Allen Initiative in Brain Health and Cognitive Impairment.
In 2025, Dr. Wang joined Van Andel Institute’s Department of Neurodegenerative Science as an assistant professor. His lab leverages multi-disciplinary methods to explore the roles of epigenetics in neurodevelopment and neurodegenerative disorders.
Dr. Wang’s research has resulted in several awards, including the 2018 Salk Innovation Award and inclusion in the Top 10 Scientific Advances in China in 2016 and 2012.
For a full list of Dr. Wang’s publications, please visit PubMed.
Co-authorships are denoted with an asterisk.
2024
Chien JF, Liu H, Wang BA, Luo C, Bartlett A, Castanon R, Johnson ND, Nery JR, Osteen J, Li J, Altshul J, Kenworthy M, Valadon C, Liem M, Claffey N, O’Connor C, Seeker LA, Ecker JR, Behrens MM, Mukamel EA. 2024. Cell-type-specific effects of age and sex on human cortical neurons. Neuron 15(7):2524 –2539.e5.
2023
Wang BA*, Jones JR*, Zhou J, Tian* W, Wu Y, Wang W, Berube P, Bartlett A, Castanon R, Nery JR, Chen H, Kenworthy M, Altshul J, Valadon J, Wang Y, Kang A, Goodman R, Liem M, Claffey N, O’Connor C, Metcalf J, Luo C, Gage FH, Ecker JR. Pre-print. Epigenome erosion in Alzheimer’s disease brain cells and induced neurons. bioRxiv.
Liu H, Zeng Q, Zhou J, Bartlett A, Wang BA, Berube P, Tian W, Kenworthy M, Altshul J, Nery JR, Chen H, Castonon RG, Zu S, Li YE, Lucero J, Osteen JK, Pinto-Duarte A, Lee J, Rink J, Cho S, Emerson N, Nunn M, O’Connor C, Wu Z, Stoica I, Yao Z, Smith KA, Tasic B, Luo C, Dixon JR, Zeng H, Ren B, Behrens MM, Ecker JR. 2023. Single-cell DNA methylome and 3D multi-omic atlas of the adult mouse brain. Nature 624:366–377.
2018
Hrit J, Goodrich L, Li C, Wang BA, Nie J, Cui X, Martin EA, Simental E, Fernandez J, Liu MY, Nery JR, Castanon R, Kohli RM, Tretyakova N, He C, Ecker JR, Goll M, Panning B. 2018. OGT binds a conserved C-terminal domain of TET1 to regulate TET1 activity and function in development. eLife 7.
2017
Zuo E*, Cai YJ*, Li K*, Wei Y*, Wang BA*, Sun Y, Liu Z, Liu J, Hu X, Wei W, Huo X, Shi L, Tang C, Liang D, Wang Y, Nie YH, Zhang CC, Yao X, Wang X, Zhou C, Ying W, Wang Q, Chen RC, Shen Q, Xu GL, Li J, Sun Q, Xiong ZQ, Yang H. 2017. One-step generation of complete gene knockout mice and monkeys by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing with multiple sgRNAs. Cell Res 27:933–945.
2016
Dai HQ*, Wang BA*, Yang L*, Chen JJ*, Zhu GC, Sun ML, Ge H, Wang R, Chapman DL, Tang F, Sun X, Xu GL. 2016. TET-mediated DNA demethylation controls gastrulation by regulating Lefty-Nodal signalling. Nature 538:528–532.
2014
Hon GC, Song CX, Du T, Jin F, Selvaraj S, Lee AY, Yen CA, Ye Z, Mao SQ, Wang BA, Kuan S, Edsall LE, Zhao BS, Xu GL, He C, Ren B. 2014. 5mC oxidation by Tet2 modulates enhancer activity and timing of transcriptome reprogramming during differentiation. Mol Cell 56:286–297.
2012
Yang H*, Shi L*, Wang BA*, Liang D, Zhong C, Liu W, Nie Y, Liu J, Zhao J, Gao X, Li D, Xu GL, Li J. 2012. Generation of genetically modified mice by oocyte injection of androgenetic haploid embryonic stem cells. Cell 149:605–617.


Jamie Durst, B.S.
Senior Administrative Assistant II, Department of Neurodegenerative Science

Karianne Reynolds
Assistant Research Technician, Department of Neurodegenerative Science

Ellianna Sempek
Research Technician, Department of Neurodegenerative Science



